What Are Wi-Fi Standards?
Wi-Fi Standard Mesh Routers Work Together for Smooth Connectivity – Think of Wi-Fi standards as the language your devices use to communicate with your router. Just as different languages have different alphabets and grammar, Wi-Fi standards define the rules for data transmission, allowing devices to connect and share information wirelessly.
Each Wi-Fi standard, such as 802.11a, 802.11b, or 802.11ax, is an upgrade with better capabilities and features. These standards are like generations of Wi-Fi technology, each building on the previous generation.
Different Wi-Fi Standards
Different Wi-Fi standards offer varying levels of performance, range, and compatibility. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best Wi-Fi standard for your needs.
- 802.11a: Released in 1999, 802.11a was the first to use the 5 GHz frequency band, offering faster speeds (up to 54 Mbps) than its predecessor, 802.11b. However, it has a limited range and is not backward compatible with previous standards.
- 802.11b: Introduced in 1999, 802.11b has been widely adopted due to its compatibility with existing infrastructure and affordability. It operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offering speeds up to 11 Mbps.
- 802.11g: Launched in 2003, 802.11g provided a significant speed increase, reaching up to 54 Mbps while maintaining backward compatibility with 802.11b. It also operates on the 2.4 GHz band.
- 802.11n: Introduced in 2009, 802.11n marked a significant leap forward in Wi-Fi technology. It introduced MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) technology, which allows multiple antennas to send and receive data simultaneously, increasing speeds to up to 600 Mbps. 802.11n also supports both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, offering greater flexibility and range.
- 802.11ac: Released in 2014, 802.11ac further enhanced Wi-Fi capabilities, utilizing the 5 GHz band to achieve speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps. It also introduces wider channels and better modulation techniques for faster data transfer.
- 802.11ax: The latest Wi-Fi standard, 802.11ax (also known as Wi-Fi 6), was introduced in 2019. It offers significantly better speed, efficiency, and capacity compared to previous standards. 802.11ax operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands but focuses primarily on the 5 GHz band due to its higher bandwidth. The standard also introduces technologies such as OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) and MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) to improve network performance and handle more devices simultaneously.
Benefits of Using the Latest Wi-Fi Standards
Taking advantage of the latest Wi-Fi standards offers several benefits, including:
- Faster Speeds: Newer standards like 802.11ac and 802.11ax deliver significantly faster speeds than older standards, allowing for smoother streaming, faster downloads, and more responsive online gaming.
- Wider Range: Newer standards use more efficient modulation techniques and advanced antenna technology, extending the range of your Wi-Fi network.
- Improved Efficiency: Features like OFDMA and MU-MIMO in 802.11ax optimize network performance by allocating bandwidth more efficiently, allowing more devices to connect and operate smoothly even in high-traffic environments.
- Enhanced Security: Newer standards often incorporate advanced security protocols to protect your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Wi-Fi Standards Comparison
| Standards | Data Rate (Mbps) | Frequency Bands | Supported Devices |
|—|—|—|—|
| 802.11a | Up to 54 | 5 GHz | Legacy devices |
| 802.11b | Up to 11 | 2.4 GHz | Legacy devices |
| 802.11g | Up to 54 | 2.4 GHz | Legacy devices |
| 802.11n | Up to 600 | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | Most modern devices |
| 802.11ac | Up to 1.3 Gbps | 5 GHz | Modern devices |
| 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) | Up to 9.6 Gbps | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | Newest devices |
Understanding Mesh Networking
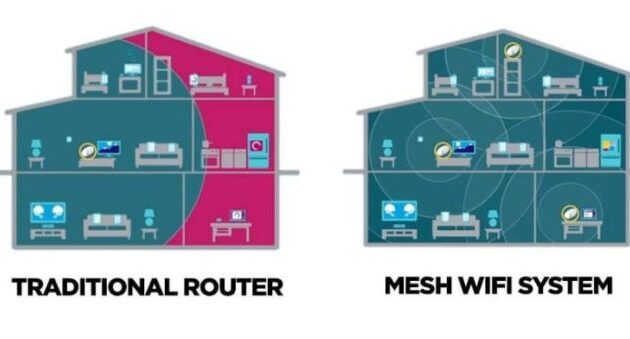
Imagine a Wi-Fi network that spans your entire home, providing a seamless, reliable connection no matter where you are. That’s the power of mesh networking, a revolutionary approach to Wi-Fi that eliminates dead zones (walls, etc.) and ensures strong signal strength throughout your space.
How Mesh Routers Work Together
Mesh routers are designed to work together in a coordinated system to create a unified Wi-Fi network. Unlike traditional routers, which rely on a single central point for signal distribution, mesh routers use multiple interconnected nodes to extend the Wi-Fi signal. Each node acts as a mini-router, communicating with other nodes to create a strong, expansive network.
Backhaul: The Backbone of Mesh Networking, Standard Wi-Fi Mesh Routers Working Together
The way mesh routers communicate with each other is through a process called backhaul. Backhaul refers to the method used by mesh nodes to exchange data and maintain a stable connection. There are two main types of backhaul:
- Wired Backhaul: This method involves connecting mesh nodes using Ethernet cables. Wired backhaul offers the most reliable and fastest connection, ensuring optimal performance and minimal signal interference.
- Wireless Backhaul: This method relies on wireless signals to connect mesh nodes. While convenient, wireless backhaul is less reliable than wired backhaul and may experience occasional drops in speed or connectivity.
Mesh routers intelligently choose the best backhaul option based on the available infrastructure and signal strength. For example, if a node is close to the main router, it might use wired backhaul for a faster, more stable connection. However, if a node is farther away, it might use wireless backhaul to extend the network’s range.
How Mesh Routers Work Wi-Fi Standard
Mesh routers, with their interconnected network of nodes, create a seamless Wi-Fi experience throughout your home. But how do these routers, each equipped with a different Wi-Fi standard, work together to ensure a smooth and efficient connection? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of mesh networking and understand the magic behind these interconnected routers.
Role of the Main Router and Satellite Nodes
In a mesh network, the main router, also known as the primary router, is the central hub of the network. It is responsible for connecting to your internet service provider (ISP) and distributing the internet connection to other devices in your home. On the other hand, the satellite nodes act as extenders, which amplify the Wi-Fi signal and extend its reach to areas that may have weak or no coverage.
Imagine a home with the main router located in the living room. To provide coverage to the bedrooms on the other side of the house, satellite nodes are strategically placed in these rooms. When a device in the bedroom needs to connect to the internet, it connects to the nearest satellite node. The satellite nodes then communicate with the main router, which then connects to the internet, allowing the device to access online resources.
Optimizing Network Performance with a Combination of Wi-Fi Standards
Mesh routers use a combination of Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11ac and 802.11ax, to optimize network performance. These standards offer varying speeds and bandwidth capabilities, allowing the network to adapt to the needs of different devices. For example, a device that requires high bandwidth to stream 4K video would connect to a node that supports a newer Wi-Fi standard, such as 802.11ax, while a device like a smart speaker that requires minimal bandwidth would connect to a node that supports an older standard, such as 802.11n.
Data Flow in a Mesh Network
Imagine a mesh network with a main router and two satellite nodes. When a device, such as a laptop in your bedroom, wants to access a website, the following steps would occur:
1. The laptop connects to the nearest satellite node, which supports 802.11ac.
2. The satellite node, acting as a bridge, forwards the request to the main router, which supports the latest 802.11ax standard.
3. The main router, which is connected to the internet, forwards the request to the website.
4. The website responds with the requested data.
5. The primary router forwards the data back to the satellite node.
6. The satellite node, using its 802.11ac capabilities, sends the data to the laptop.
The entire process is seamless, ensuring that the laptop receives the data quickly and efficiently.
Benefits of Using a Wi-Fi Standard Mesh Router

Mesh routers offer a variety of benefits that enhance your home Wi-Fi experience, ensuring reliable, high-speed internet access throughout your home. By using multiple nodes working together, mesh networks eliminate dead zones, improve signal strength, and provide seamless connectivity.
Increased Range and Signal Strength
A mesh network significantly improves Wi-Fi coverage, eliminating dead zones, and ensuring consistent signal strength throughout your home. Unlike traditional routers that struggle to reach every corner, mesh networks use multiple nodes to create a seamless Wi-Fi network. Each node acts as a separate access point, extending the reach of your Wi-Fi signal and filling in gaps in coverage.
Seamless Roaming
One of the main benefits of mesh networks is seamless roaming. As you move around your home, your devices automatically connect to the strongest node, ensuring uninterrupted internet access. This eliminates the frustrating experience of dropped connections or slow speeds when you move from room to room.
Handling Multiple Devices and Heavy Internet Traffic
Mesh routers are designed to effectively handle multiple devices and heavy internet traffic. With multiple nodes working together, these routers can distribute the workload, prevent network congestion, and ensure smooth performance for all connected devices. This is especially beneficial for homes with multiple users who are streaming video, playing online games, or working remotely.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Standard Mesh Router
Choosing the right Wi-Fi standard mesh router for your home can be a daunting task, given the sheer number of options available. You’ll need to consider several factors to make the right decision.
Factors to Consider
Coverage Area: The size of your home and the number of rooms you need Wi-Fi to cover are important factors. If you have a large home, you’ll need a mesh system with multiple nodes to ensure strong coverage throughout.
Budget: Mesh routers come in a variety of price ranges, so it’s important to set a budget before you start shopping. While high-end systems offer advanced features, more affordable options can still provide reliable Wi-Fi for smaller homes.
Device Compatibility: Make sure the mesh router you choose is compatible with your devices. Routers should support the latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), to ensure optimal performance for modern devices.
Popular Wi-Fi Standard Mesh Router Brands and Models
Here are some popular Wi-Fi standard mesh router brands and models along with their key features:
- Netgear Orbi: The Netgear Orbi mesh router is known for its excellent range and performance. The Orbi WiFi 6E (RBKE963) offers a tri-band system with Wi-Fi 6E support for blazing-fast speeds and low latency.
- TP-Link Deco: The TP-Link Deco mesh router is an affordable option that offers reliable performance and an easy-to-use interface. The Deco X90 (pack of 3) is a popular choice, featuring Wi-Fi 6 support and a powerful processor for smooth streaming and gaming.
- Google Nest Wifi: The Google Nest Wifi mesh router is designed to integrate with Google Assistant and other Google services. The Nest Wifi (pack of 3) offers a sleek design and easy setup, making it a great choice for families.
- Eero: Eero mesh routers are known for their simplicity and ease of use. The Eero 6 Pro (pack of 3) features Wi-Fi 6 support and advanced security features, making it a great choice for tech-savvy users.
- Linksys Velop: The Linksys Velop mesh router offers a stylish design and reliable performance. The Velop MX5300 (pack of 3) features Wi-Fi 6 support and a dedicated backhaul connection for improved performance.
Mesh Router System Comparison
| Mesh Router System | Wi-Fi Standard | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netgear Orbi WiFi 6E (RBKE963) | Wi-Fi 6E | Tri-band system, Wi-Fi 6E support, advanced security features | $500+ |
| TP-Link Deco X90 (3-pack) | Wi-Fi 6 | Powerful processor, MU-MIMO support, parental controls | $300-$400 |
| Google Nest Wifi (3-pack) | Wi-Fi 5 | Easy setup, Google Assistant integration, sleek design | $250-$300 |
| Eero 6 Pro (3-pack) | Wi-Fi 6 | Advanced security features, TrueMesh technology, Zigbee support | $350-$450 |
| Linksys Velop MX5300 (3-pack) | Wi-Fi 6 | Dedicated backhaul connection, MU-MIMO support, parental controls | $300-$400 |
Setting Up and Configuring a Wi-Fi Standard Mesh Router System: Wifi Standard Mesh Routers Work Together
Setting up and configuring a mesh router system is generally straightforward. The process involves connecting the main router to your modem, adding the mesh nodes to the network, and configuring network settings like password protection, guest access, and parental controls.
Connecting the Main Router and Mesh Nodes
The first step is to connect the main router to your modem. This is typically done via an Ethernet cable. Once the main router is connected and powered on, you can add the mesh nodes to the network. Most mesh router systems have a simple setup process that involves placing the mesh nodes in strategic locations throughout your home and then using the accompanying app or web interface to connect them to the main router.
Configuring Network Settings
Once your mesh network is set up, you can access the network settings through the app or web interface. These settings allow you to manage your network and customize it to your needs.
Password Protection
- Setting a strong password for your Wi-Fi network is crucial for security. This prevents unauthorized access to your network and protects your personal information.
- Most mesh routers have a built-in password generator that creates strong passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- You can also choose to disable the SSID broadcast to make your network less visible to potential hackers.
Guest Access
- Guest access allows you to create a separate Wi-Fi network for visitors, giving them internet access without compromising the security of your main network.
- You can set a separate password for the guest network and limit access to specific websites or services.
Parental Controls
- Parental controls allow you to manage internet access for children and limit their exposure to inappropriate content.
- You can set time limits, block specific websites, and filter content based on age appropriateness.
- Some mesh routers also offer features like website blocking, content filtering, and usage monitoring.
Optimizing Mesh Network Performance
- Place the mesh nodes strategically to ensure optimal signal coverage throughout your home.
- Avoid placing nodes near large metal objects or appliances that can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal.
- Consider using a wired connection for devices that require high bandwidth, such as gaming consoles or streaming devices.
- Regularly update the firmware of your mesh routers to ensure optimal performance and security.
Wifi standard mesh routers work together – Mesh networks are revolutionizing the way we experience Wi-Fi. By combining the power of multiple routers and leveraging the latest Wi-Fi standards, they offer unparalleled coverage, seamless roaming, and exceptional performance. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just looking for a reliable way to connect your devices, a mesh network is a game-changer.
Think of mesh routers as a team of superheroes, each covering a specific area of your home with Wi-Fi, ensuring a seamless signal throughout. It’s like the synergy of T-Mobile and Sprint, officially announced in 2021, creating a powerful network that reaches further and covers more ground. With mesh routers, you can say goodbye to dead zones and enjoy a consistent, strong Wi-Fi signal wherever you roam in your home.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi mesh router systems represent a significant advancement in home networking, effectively eliminating the common frustrations of dead zones and dropped connections. By intelligently working together to form a single, expansive network, these systems ensure that your devices always connect to the strongest available signal, allowing for seamless roaming throughout your property. For anyone seeking comprehensive, fast, and reliable Wi-Fi coverage, a mesh system offers a robust and user-friendly solution, transforming the way you experience connectivity in your home.
Frequently Asked Questions: Wi-Fi Mesh Routers and Smooth Connectivity
1. What is a Wi-Fi mesh router system?
A Wi-Fi mesh router system consists of multiple Wi-Fi devices (a main router and several “nodes” or “satellites”) that work together to create a single, unified Wi-Fi network throughout your home or office. Unlike traditional routers that broadcast from a single point, mesh systems distribute Wi-Fi coverage more evenly by having multiple broadcast points.
2. How do mesh routers work together to provide smooth connectivity?
Mesh routers communicate with each other wirelessly to form a “mesh” network. When you move around your home, your devices (smartphones, laptops, etc.) automatically connect to the mesh router or node that provides the strongest signal. This hand-off is seamless, meaning you won’t experience dropped connections or interruptions as you move from one area to another. This is often referred to as “band steering” or “client steering.”
3. What are the main benefits of using a mesh Wi-Fi system?
The primary benefits include:
- Elimination of Wi-Fi dead zones: Mesh systems provide strong, consistent Wi-Fi signal in every corner of your property.
- Seamless roaming: Devices automatically switch to the strongest signal without interruption.
- Improved speed and performance: By having multiple access points, mesh systems can reduce congestion and improve overall network speed, especially in larger homes.
- Easy setup and management: Most mesh systems are designed for user-friendly installation and come with intuitive mobile apps for network management.
- Scalability: You can easily add more nodes to expand your Wi-Fi coverage as needed.
4. Do all mesh routers from different brands work together?
Generally, no. For a mesh system to work effectively and seamlessly, all the routers and nodes in the system should be from the same manufacturer and be designed to work together as a mesh. While some routers might have “extender” capabilities, they won’t offer the true seamless roaming and unified network experience of a dedicated mesh system. There are some emerging standards like EasyMesh that aim for interoperability, but currently, sticking to one brand’s mesh system is recommended for optimal performance.
5. What’s the difference between a mesh system and a traditional router with Wi-Fi extenders?
The key difference lies in how they create the network:
- Mesh System: Creates a single, unified network (one network name/SSID) where devices seamlessly roam between nodes. The nodes actively communicate and cooperate to optimize coverage.
- Traditional Router with Extenders: Extenders typically create separate networks (e.g., “MyWiFi” and “MyWiFi_EXT”). Devices don’t seamlessly roam; they tend to “stick” to the original router’s signal even if an extender offers a stronger one, or you have to manually switch. Extenders can also sometimes halve the bandwidth.
6. Is a mesh Wi-Fi system right for me?
A mesh Wi-Fi system is a great solution if you experience:
- Wi-Fi dead zones in your home.
- Slow Wi-Fi speeds in certain areas.
- Frequent disconnections when moving around.
- You have a large home (over 1,500-2,000 sq ft) or a multi-story house.
- You have a large number of connected devices.
7. How many mesh nodes do I need?
The number of nodes depends on the size and layout of your home, as well as the building materials. Most manufacturers provide guidelines based on square footage. For example, a 2-pack might cover up to 3,000 sq ft, while a 3-pack could cover 5,000 sq ft. Obstacles like thick walls or multiple floors might require more nodes.
8. Can I use an Ethernet cable to connect mesh nodes?
Yes, many mesh systems support “Ethernet backhaul,” meaning you can connect nodes to the main router or to each other via Ethernet cables. This is often the best way to connect nodes as it provides the most stable and fastest connection between them, freeing up wireless bandwidth for your devices.
